All Grant Agreements should be effective by March 31, 2006.
Deadline for disbursement of DGF grants is May 31, 2006.
What is the Development Grant Facility?
The Development Grant Facility (DGF) is the Bank’s mechanism for providing grant funding for global and regional development initiatives which are of high value for our client countries but cannot be supported adequately through regular country-based operations. The DGF was established in 1997 to integrate the overall strategy, allocations, and management of Bank grant-making activities funded from the Administrative Budget under a single umbrella mechanism. DGF grants are intended to encourage innovation, catalyze partnerships and broaden the scope of Bank services.
World Bank Site for the Development Grant Facility
What is the purpose of the DGF under EITI?
The DGF grants for EITI purposes are open to civil society organizations involved in promoting the transparency agenda in the extractive industries. Examples of organizations eligible for funding include non-governmental organizations, community-based organizations, academic institutions and media. The activities of these organizations and their proposed DGF program must meet the DGF criteria.
How does our organization apply?
All grant applications must be sponsored by a unit within the Bank on behalf of an external recipient to ensure consistency with Bank priorities; DGF does not accept applications directly from external entities. DGF applications concerning the EITI are sponsored by the Oil, Gas, Mining and Chemicals Department of the World Bank. Please send your application to the following members of the department: Bermet Sydygalieva ([email protected]) and Esther Petrilli-Massey ([email protected]).
What kind of documentation does our organization need to submit?
Prior to disbursement:
- Program Suggestion: Clearly identify how the program entails capacity building activities, or otherwise contributes to implementation of EITI in a country. The description of the program should include a timeline, and key activities to be carried out. It should also explain results expected from the implementation of the program, and resources necessary to implement the grant.
- Description of the Organization: Show a record of achievement in the program area, and financial probity. This also includes sound financial management and administration (eg. financial statements for the past 12-36 months). Financial accounts are for internal due diligence purposes only, and serve as a basis for the Task Manager’s decision whether or not to disburse the grant. Should a decision be made that a grant would be allocated to this organization, the organization should submit its bank account details for the grant funds transfer to take place.
- Budget: Identify the importance of Bank Funds (indicate the percentage of the of the total budget to be financed by the DGF grant).). It is suggested that the proposed budget include all taxes, bank, and audit charges applicable in the recipient country, unless otherwise agreed.
- Disengagement plan: Show how the organization plans to phase out or replace the funding from the DGF over maximum three years. This should include a monitorable plan with milestones of disengagement.
- Key Staff: Include resumes of those staff who will be directly involved in the implementation of the suggested program, and their experience relevant to the proposed activity.
After disbursement:
In accordance with the Grant letter the following should be completed at the end of the annual year.
- Audit:
- The Recipient shall maintain or cause to be maintained a financial management system, including records and accounts, and prepare financial statements in accordance with consistently applied accounting standards acceptable to the Bank, adequate to reflect the operations, resources and expenditures related to the Program.
- The Recipient shall: (i) have the financial statements referred to in subparagraph (a) above for each such fiscal year (or other period agreed to by the Bank), audited, in accordance with consistently applied auditing standards, acceptable to the Bank, by independent auditors acceptable to the Bank; (ii) furnish to the Bank as soon as available, but in any case not later than three months after the end of each such year (or such other period agreed to by the Bank), (A) certified copies of the financial statements referred to in subparagraph (a) above for such year (or such other period agreed to by the Bank), as so audited, and (b) an opinion on such statements by said auditors, in scope and detail satisfactory to the Bank; and (iii) furnish to the Bank such other information concerning such records and accounts and the audit of such financial statements, and concerning said auditors, as the Bank shall have reasonably requested.
- An exemption to the obligatory audit requirement in (b) may be provided for grants below US$50,000. Should an audit exemption be granted, a clause should be included in the Grant Letter of Agreement reflecting the exemption.
- Reports:
Not later than four months from the end of the grant period, the Recipient shall submit to the Bank a report summarizing the activities financed by the Grant and assessing the results achieved by the activities compared to their objectives.
How do we find out if our organization is qualified?
For more information, please see the Eligibility Criteria for the Development Grant Facility.
Where Can We Get More Information?
Please submit any questions to Bermet Sydygalieva ([email protected]), Telephone: 202-458-9357 and Esther Petrilli-Massey ([email protected]), Telephone: 202-473-1949.
Main Points for Eligibility for DGF Grants:
LEGAL ENTITY
- The Organization that receives the funds has to be a legal entity. The Bank will enter a contractual relation with the organization, thus it has to have established its financial property.
FOLLOW BANK OBJECTIVES AND DOESN’T COMPETE WITH REGULAR INSTRUMENT
- The program contributes to furthering the Bank’s development and resource mobilization objectives in fields basic to its operation, but it does not compete with or substitute for regular Bank instruments. These should address new or critical development problems, and clearly distinguishable from the Bank’s regular programs.
FOLLOW THE COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE OF THE BANK
- The Bank has a distinct comparative advantage in being associated with the grant program –not replicating role of other donors.
MULTI-COUNTRY BENEFIT, OR CAPACITY BUILDING ACTIVITIES
- The program encompasses multi-country benefits. In cases of single country grants, the program will encompass capacity-building activities, where this is a significant part of the Country Assistance Strategy, and cannot be supported by other Bank instruments or by other donors.
PROVIDES LEVERAGE TO GENERATE OTHER FINANCIAL SUPPORT
- The Bank’s presence provides significant leverage for generating financial support from other donors (that is, Bank involvement should provide assurance to other donors of program effectiveness as well as sound financial management and administration.)
FINANCIAL AND QUALITATIVE STANDING OF THE ORGANIZATION
- The Grant is normally given to an institution with a record of achievement in the program area and financial probity. The quality of the activities and competence of management are important considerations.
MUTUAL INDEPENDENCE
- The management of the recipient institution is independent of the Bank Group’s. An arm’s length relation is essential – yet the bank may have a role in the governance of the institution through membership in its governing board or oversight committee. If the recipient’s programs are highly innovative or experimental, Bank involvement in supporting the recipient in execution is allowed.
DISENGAGEMENT STRATEGY
-
Grant proposal are expected to incorporate an explicit disengagement strategy. Monitorable action steps should be outlined indicating milestones and targets for disengagement. Disengagement should be done within three years. It is the task managers responsibility to ensure that recipients understand and accept DGF funding on this basis. Letters of agreement should therefore reflect these requirements. The Bank’s disengagement should have minimal disruption to an ongoing program or activity. The latter can be done through: reduction of activities, handing reins to other partners, commercializing services, or mainstreaming the activity into the Bank.
PROMOTE AND REINFORCE PARTNERSHIPS
- The activities and programs financed under the DGF should promote and reinforce partnerships with key partners in the development arena.


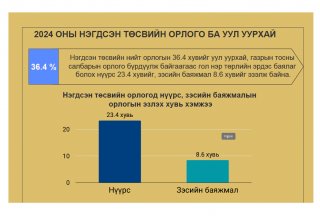
 Naranchuluun
Naranchuluun